KIELTYKA GLADKOWSKI TOOK PART IN SEMINAR ON RUSSIA EXPORT CONTROLS AND DUAL-USE TECHNOLOGY
Publication date: October 25, 2023
On 25 October 2023, KIELTYKA GLADKOWSKI took part in the seminar organised by Sayari on Russia Export Controls and Dual-Use Technology: Mitigating Diversion Risk.
Russia continues to rely on Western-manufactured dual-use technology to produce advanced weapons systems and rearm its military. And while a number of countries have taken steps to curb the exporting of critical technology to Russian end users, public reporting, recent designations, and law enforcement actions shed light on intricate sanctions evasion schemes designed to procure needed technology.
The seminar analysed Russian trade data and discussed recent trends in dual-use technology procurement, and demonstrated how regulators and industry can leverage public and commercially available data to mitigate end-user risk and enhance enforcement.
The specific topics discussed were:
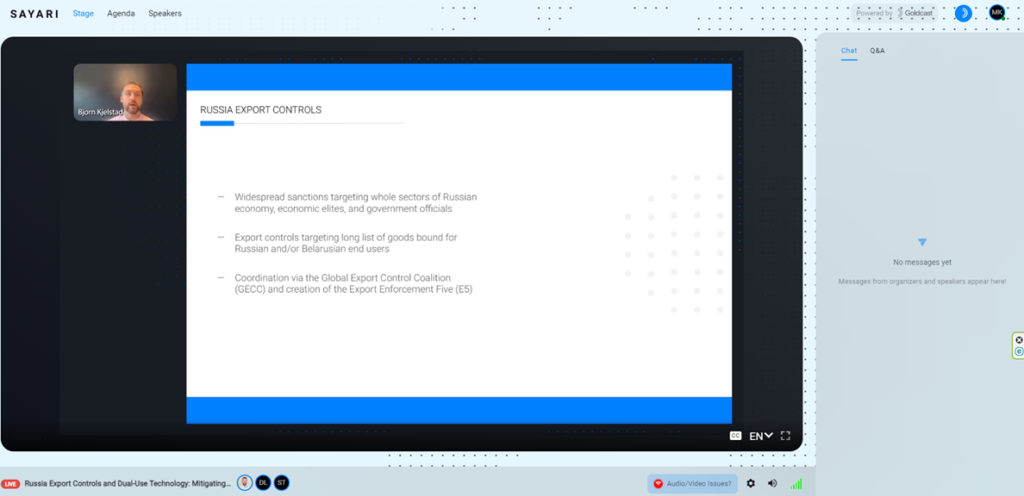
– Recent actions taken by the Export Enforcement 5 (E5) and the Global Export Control Coalition (GECC) to curb exports of dual-use goods to Russia
– Common typologies employed by procurement networks to circumvent export controls
– Trends in dual-use technology flows to Russia, according to 2023 Russian and global trade data
– Case studies demonstrating how public and commercially available data can be used to identify end-user risk and enhance investigations into potential evasion of export controls.
The speakers were: Bjorn Kjelstad, Director of Training & Investigations and David Lynch, Global Head of Analytical Solutions.
The subject matter of the seminar helps our lawyers to provide more knowledgeable assistance within sanctions and risk involved, assessment of carrying our transactions and public procurement from opaque jurisdictions, transshipment via third countries, sanctions’ jurisdictional scope and impact, asset freezing measures, ownership by sanctioned persons, the interpretation of sectoral sanctions, contractual force majeure and termination issues affecting contracts with sanctioned counterparties.
The seminar, in particular, shed more light to the dual use technologies (both for civilians and for defence industry) and questioned transactions and shipments to Russia that were traced by Sayari based on collected data.
There has also been discussed the package of sanctions and export controls E5. In a coordinated effort to counter Russia’s aggression against Ukraine, the Export Enforcement Five (E5) — comprising Australia, Canada, New Zealand, the United Kingdom, and the United States — have released unprecedented packages of sanctions and export controls. These measures aim to impose economic costs on Russia, degrade its war capabilities. For businesses, failure to understand the evolving export controls sanctions environments and conduct due diligence on partners can result in reputational harm, future business relationship challenges, fines, and/or criminal charges. Special guidance in this respect was issued by the Bureau of Industry Security (BIS), the E5, and the Exporting Commercial Goods Guidance for Industry and Academia.
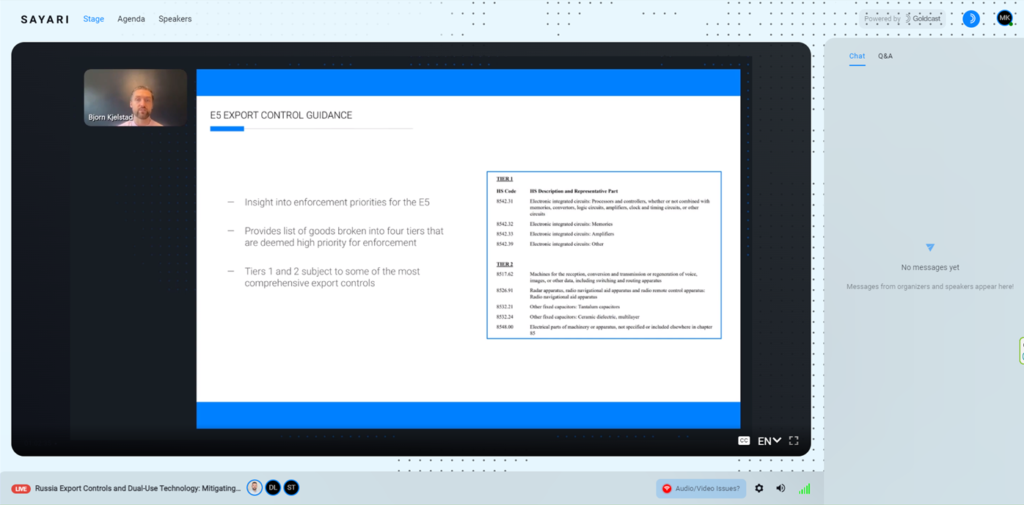
The E5’s High Priority Items List is primarily based on the Harmonized System (HS) Code classification of Russian weapons system components recovered on the battlefield in Ukraine. Items described by these HS codes have been found in multiple Russian weapons systems used against Ukraine, including the Kalibr cruise missile, the Kh-10 cruise missile, and the Orlan-10 UAV.
The E5, in collaboration with international partners, including the EU and Japan, has prioritized controlled items in a list of 45 HS codes. These codes include electronic components such as integrated circuits and radio frequency (RF) transceiver modules critical to Russian weapons systems. The list is divided into four tiers, ranked according to their criticality:
Tier 1: Integrated circuits (microelectronics)
Tier 2: Electronics related to wireless communication, satellite-based radio navigation, and passive electronic components
Tier 3: Divided into electronic and non-electronic items to provide greater clarity to the different industries that may work with these items
Tier 4: Manufacturing, production, and quality testing equipment of electric components and circuits.
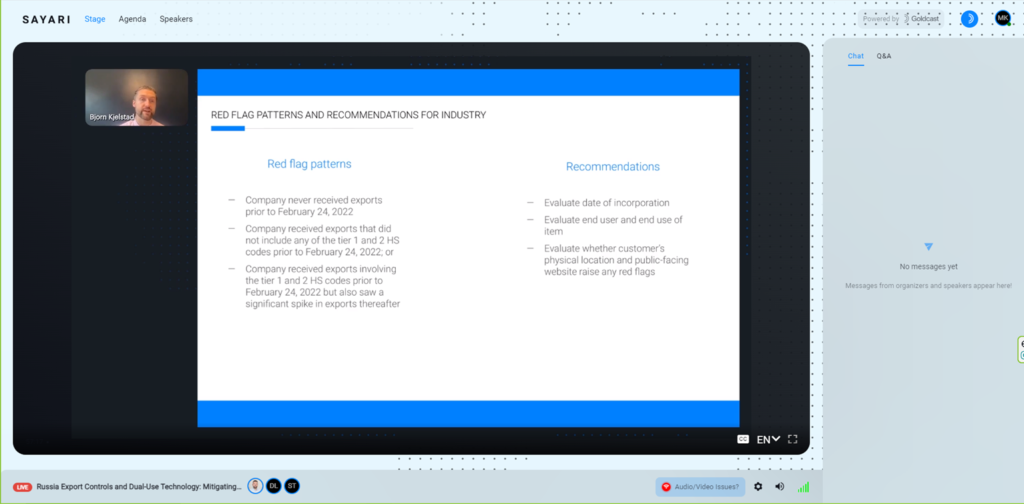
The seminar also discussed red flags and examples in trading, like when the company never received exports prior to 24 February 2022, or the company received exports that did not include any of the tier 1 and 2 HS codes prior to 24 February 2022.
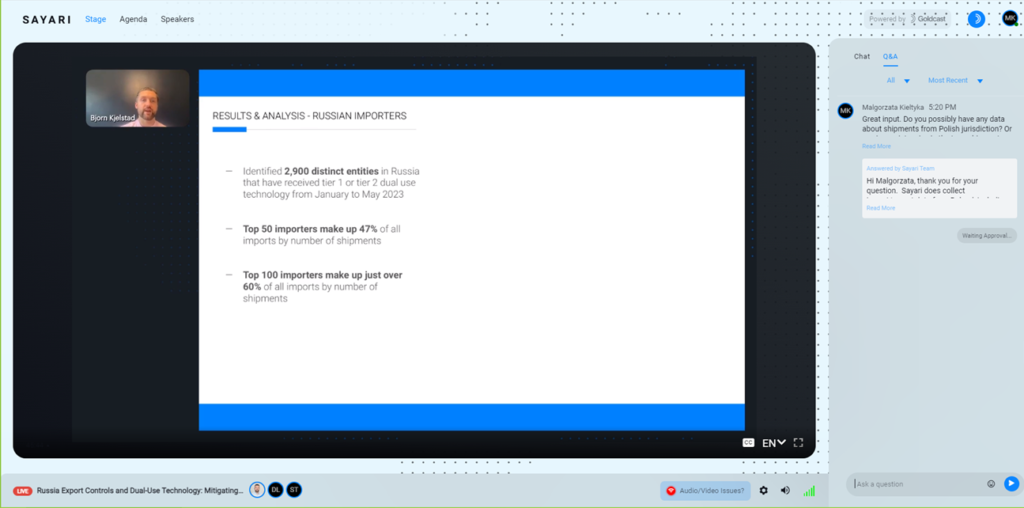
Our lawyers asked questions about the Polish jurisdiction and any transshipments to Russia:
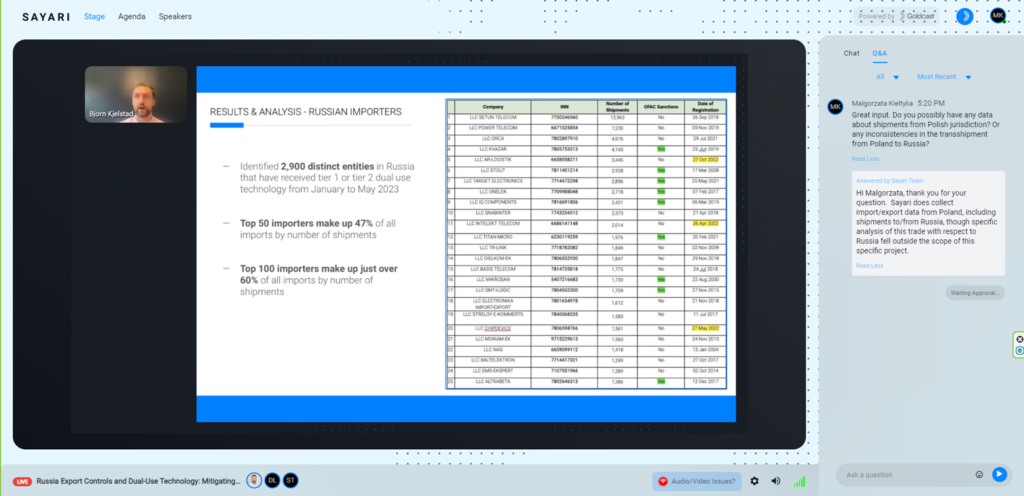
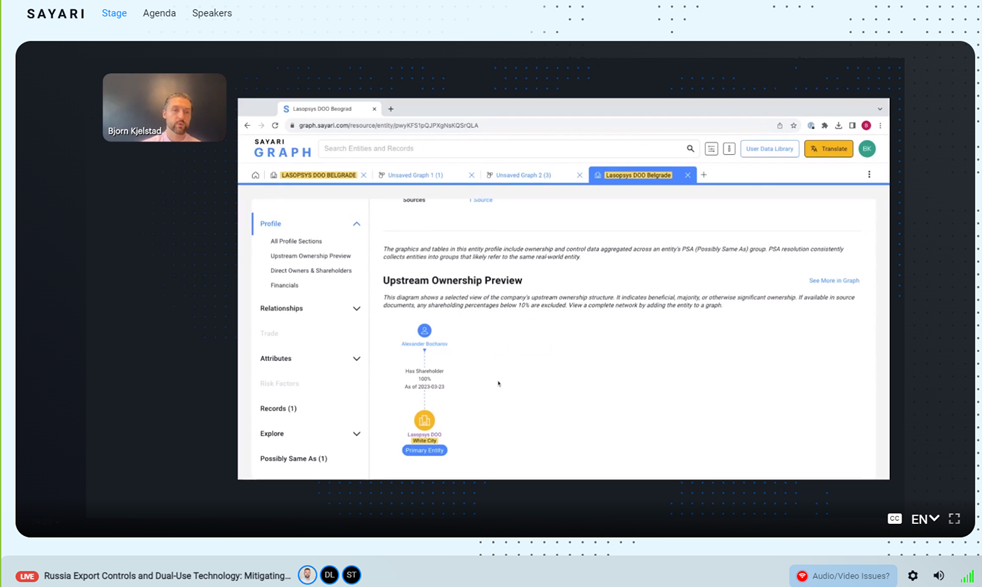
There were discussed examples of shell companies and trading from opaque jurisdiction, as well as examples of exchanging board members after the Russian invasion, like an example of replacing Russian shareholder with Polish citizen in the company whose dealings were analysed:
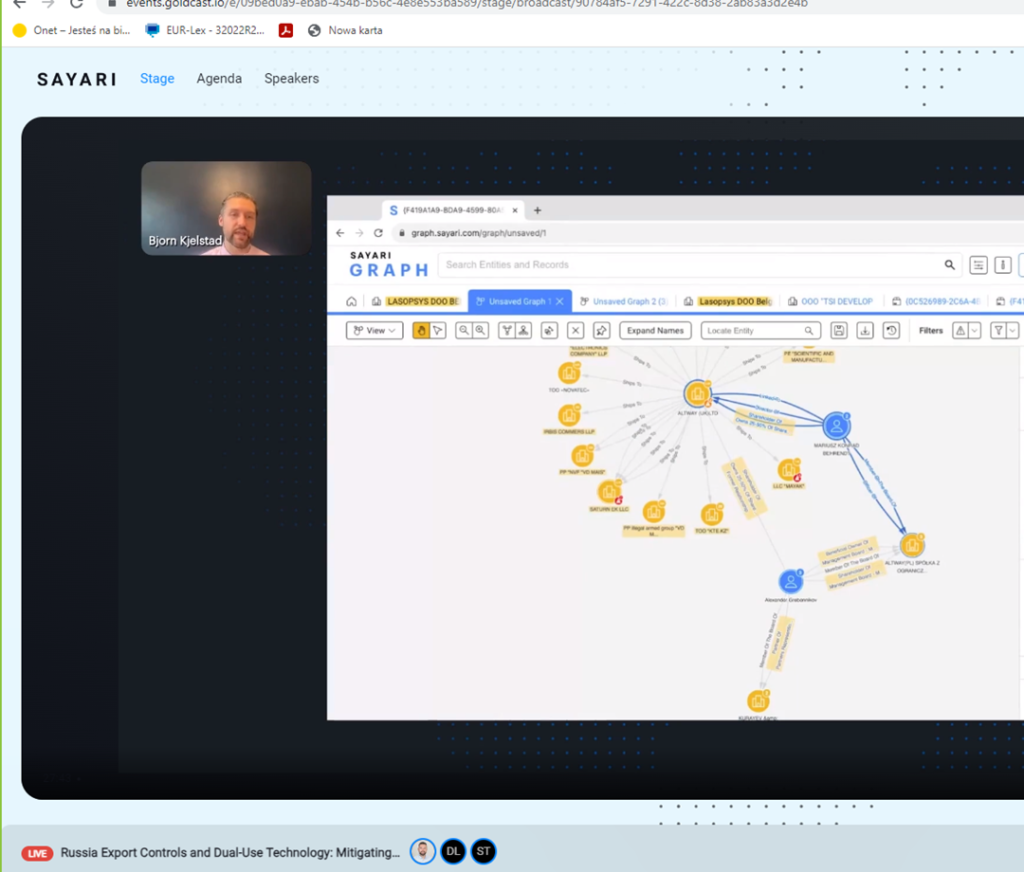
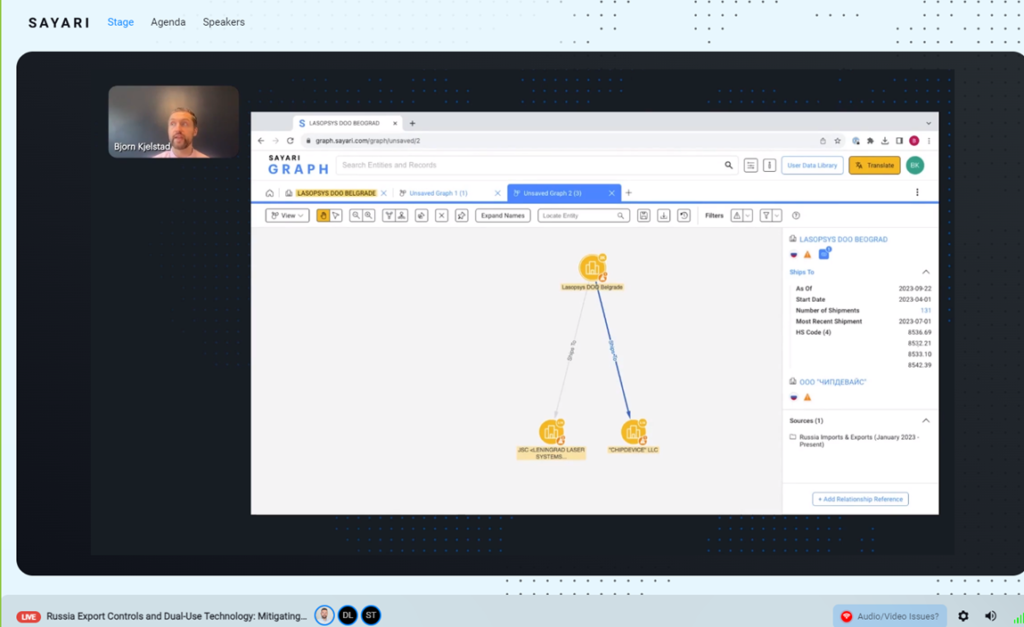
Example of shipment of high priority dual use technology to Russia:
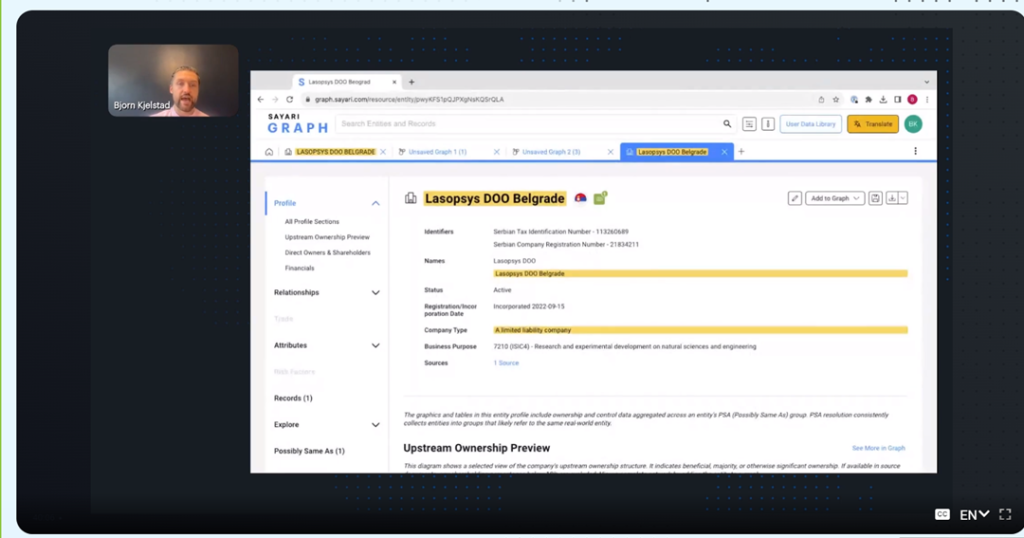
Lasopsys was incorporated within few months after invasion. It is owned by Russian citizen.