Letter of credit as a form of security for payments in international transactions
Bearing in mind the universality of international transactions and the risks that entrepreneurs face, the letter should pay attention to risk-reducing methods offered by banks. Paweł Dyrduł, associate lawyer from the law firm KG Legal Kiełtyka Gładkowski Professional Partnership based in Krakow, discusses the instrument of the letter of credit as a form of payment as well as the form of limiting the risk involved with transactions.
The essence of international trade
Progressive globalization has imposed on domestic companies – even on local ones – relationships with other international companies. Examples of such a connection, which may be either direct or indirect, include: competition with foreign entities, adaptation of manufactured products to international standards, the use of developed and implemented technological and management solutions.
An international commercial transaction is a transaction involving a cross-border element, so it comes down to transactions between entities based in different countries. Foreign trade can be considered in two perspectives: narrow and broad. In the narrow sense, the subject of foreign trade is material goods. Broad sense includes, for example, current and assets and credit turnovers, purchase of goods and intangible services.
Risk in international trade
Conclusion of foreign trade agreements carries different risks for the parties participating in the transaction. The most common are:
- payment risk (refusal to pay),
- currency risk (uncertainty of the exchange rate),
- commercial risk (insolvency of the contractor),
- contractual risk (refusal to receive the goods, termination of a contract by a contractor),
- risk of loss of goods,
- risk of product destruction.
Due to the increasing role of international trade, there is a need to develop safe methods of financing transactions. A clearing instrument allowing businesses to secure financing of transactions is a documentary letter of credit. It was regulated by the international standard UCP 600, which was issued in 2007 by the International Chamber of Commerce in Paris.
INCOTERMS 2000
Terms of delivery in foreign trade were developed by the International Chamber of Commerce in Paris and are called INCOTERMS 2010. INCOTERMS apply to sale contracts and, by analogy, to delivery contracts. There are eleven formulas altogether. Seven of them apply to all modes of transport, and four of them apply to maritime and inland waterway transport.
The rules for all modes of transport are:
- EXW – Ex Works
- FCA – Free Carrier
- CPT – Carriage Paid To
- CIP – Carriage And Insurance Paid To
- DAT – Delivered At Terminal
- DAP – Delivered At Place
- DDP – Delivered Duty Paid
In turn, the following rules are distinguished for maritime and inland waterway transport:
- FAS – Free Alongside Ship
- FOB – Free On Board
- CFR – Cost And Freight
- CIF – Cost Insurance Freight
Documentary letter of credit as a form of payment security
Documentary letter of credit is one of the forms of risk protection. This is a way to secure payments. It is a self-imposed obligation of the importer bank to pay (or guarantee payment) a certain amount of money to the exporter in return for submitting documents by the deadline specified in the letter of credit.
Confirmed letter of credit is even more secure for the transaction. The bank confirming the documentary letter of credit added to it a confirmation (at the order of the opening bank – the importer’s bank). This means that the bank obliges itself to pay a due amount of money to the exporter.
There are four participants in the process of settling the transaction with a letter of credit:
- applicant/orderer,
- issuing bank,
- advising bank/negotiating bank/confirming bank,
- exporter.
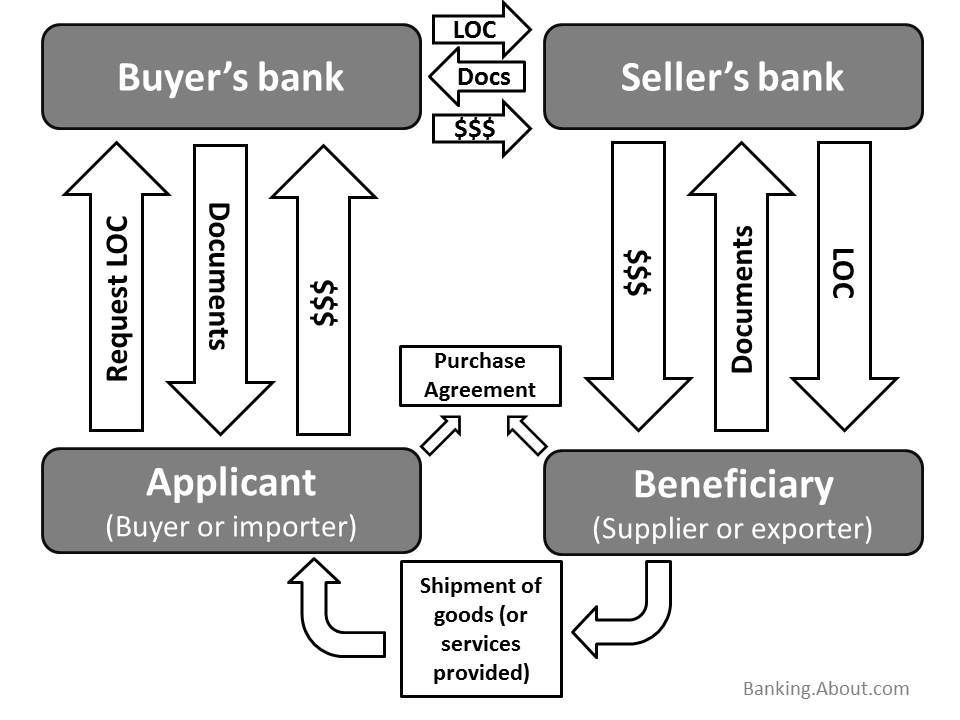
Payment settlement scheme
The process of settling transactions with a letter of credit is presented in the following diagram:
- The parties to the agreement conclude a settlement of the transaction by means of a letter of credit;
- The importer instructs his bank to open a letter of credit;
- The issuing bank notifies the exporter’s bank of the opening of the letter of credit;
- The exporter receives the letter of credit;
- The exporter sends the goods and presents the documents to his bank;
- The exporter’s bank transfers the documents to the importer’s bank;
- The importer receives the documents;
- The importer’s bank transfers the money to the exporter’s bank and the exporter’s bank pays the funds to the exporter.
Advantages and disadvantages of a letter of credit
The viability of settling transactions through a letter of credit can be viewed in terms of advantages and disadvantages by analysing the situation of both transaction participants. The list of advantages and disadvantages divided as per participants in the transaction is presented in the table below:
| Party | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Importer | · Payment will be made only for the documents indicated in the agreement
· Bank checks the documents submitted by the exporter · Confidence in delivery at designated time |
· Cash block for a specified period of time
· The costs of opening a letter of credit are burdensome · There is uncertainty as to the fulfillment of the contractual obligations of the exporter |
| Exporter | · Guarantee of receipt of payment provided that the terms of the contract are met
· Can get early payment (discounting the termination) · Ability to use a letter of credit as a means of payment for his contractors · A letter of credit may be the basis for a loan to finance the production or purchase of a product |
· Difficulty, nuisance in completing documents within the required time limit |
Letter of credit in Polish banks
Polish entrepreneurs can use the settlement of transactions by means of a letter of credit. It is offered by banks operating in the Polish market. Details of charges can be found in the tables of fees and commissions published on the respective bank’s websites.
Abstract: International transactions, letter of credit, security of payment
The article was prepared by KG LEGAL KIEŁTYKA GŁADKOWSKI based in Cracow, Poland, specialising in cross border cases, with its focus on investments in Poland, new technologies, IT and life science. It discusses payment risk in international trade and a letter of credit as one of the most popular forms of security for payments in international transactions.
Paweł Dyrduł, associate lawyer (specializing in banking law, financial law) from KG LEGAL KIEŁTYKA GŁADKOWSKI – PROFESSIONAL PARTNERSHIP based in Cracow, specializing in cross border issues and servicing life science and IT companies, discusses the essence of international commercial transactions, the risk they carry for both parties as well as a documentary letter of credit as the most common way of settling and reducing the risk in such transactions.